Introduction
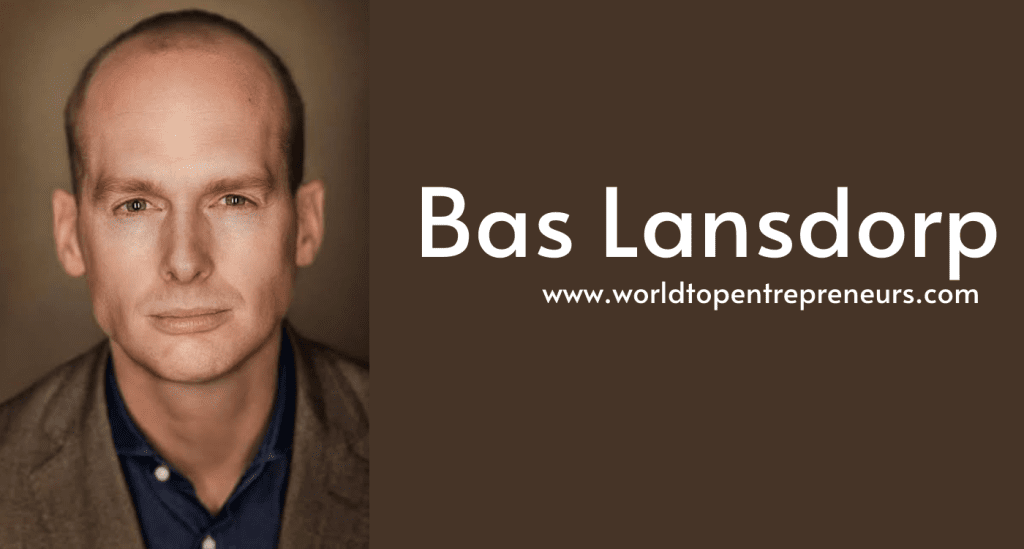
Bas Lansdorp is a Dutch entrepreneur, visionary, and one of the key figures behind Mars One, an ambitious and revolutionary project aiming to establish a human settlement on Mars. With his bold vision of sending humans to Mars, Lansdorp has sparked both excitement and skepticism about the future of space exploration and humanity’s ability to live beyond Earth. Through Mars One, Lansdorp sought to turn what was once science fiction into reality by creating a permanent human presence on the Red Planet.
In this blog, we will dive deep into Bas Lansdorp’s background, the inception of Mars One, the challenges of space exploration, and how Lansdorp’s leadership played a significant role in attempting to make Mars colonization a reality.
Who is Bas Lansdorp?
Bas Lansdorp was born in the Netherlands and is a graduate in engineering physics. His background in technology and his fascination with space led him to pursue a career that combined his passion for science with his entrepreneurial drive. Before launching Mars One, Lansdorp worked in the energy sector, focusing on innovative projects in the field of renewable energy. However, his true calling lay in space exploration, where he envisioned a future where humans could venture beyond Earth.
In 2011, he founded Mars One, which would later become one of the most audacious plans in human history: to establish a human colony on Mars. Inspired by the potential of technological advancements and the dream of interplanetary exploration, Lansdorp set out to create a project that would forever change the way humans perceive space travel.
The Vision Behind Mars One
Mars One was founded with one primary goal: to establish a permanent human settlement on Mars. The project aimed to send four astronauts on a one-way trip to Mars, where they would work together to build a sustainable colony. Unlike traditional space missions that have focused on short visits to the Moon or Mars, Mars One set out to make human settlement on Mars a permanent reality.
The idea behind Mars One was driven by several key principles:
- Self-Sustainability: The settlers would rely on technology and renewable resources to survive on Mars. The plan included creating habitats capable of producing food, water, and energy, as well as systems for recycling waste and air.
- One-Way Mission: The astronauts would never return to Earth, making the mission fundamentally different from other space programs. This one-way trip was seen as both a challenge and an opportunity to push the boundaries of human exploration.
- Public Engagement: Mars One also aimed to involve the global public in the process. The project was intended to capture the imagination of millions and bring the dream of Mars colonization closer to reality. Public interest was fueled by an open application process for astronauts and the goal of broadcasting the mission in real time.
Lansdorp’s vision for Mars One was not only to send humans to Mars but to do so in a way that was both sustainable and transformative for humanity. He believed that space exploration could be a unifying force, capable of inspiring generations and advancing the frontiers of science and technology.
The Mars One Mission: Key Milestones and Achievements
Mars One generated significant public interest when it was first announced, and the project attracted attention from both the space industry and the general public. Over the years, the mission underwent various stages of development, each marked by significant challenges and milestones.
1. Astronaut Selection
One of the first steps in the Mars One mission was selecting astronauts. Unlike traditional space agencies that choose astronauts from within established space programs, Mars One opened up applications to the public. This move created a huge global following, with thousands of individuals from around the world applying to become part of the Mars mission.
Through a series of interviews and evaluations, the Mars One team narrowed down the applicants, eventually selecting a pool of candidates who were physically and mentally prepared for the extreme conditions of living on Mars. The selection process, which was widely publicized, helped ignite a global conversation about space exploration and human missions to Mars.
2. Partnerships with Space Agencies and Companies
To achieve its goal of sending humans to Mars, Mars One needed to collaborate with established space agencies and companies. Lansdorp and his team worked to secure partnerships with private companies, including aerospace giants like Lockheed Martin and SpaceX, as well as other firms specializing in technology and innovation.
These partnerships were essential for developing the technologies required for a Mars mission, including spacecraft, habitat modules, and life-support systems. Although Mars One struggled with financial backing and faced some criticism for not securing enough support from major space agencies, these collaborations were crucial to moving the project forward.
3. Technological Development
Mars One’s mission was heavily dependent on developing technologies that could ensure the survival of astronauts on Mars. This included creating life-support systems that could sustain humans in the harsh Martian environment. The technology would need to address the challenges of limited resources, such as air, water, and food, while also ensuring that the astronauts could perform tasks like construction, scientific research, and communication with Earth.
The development of these technologies was expected to be carried out in stages, starting with unmanned missions to Mars before sending humans. While Mars One managed to secure some investments and collaborators, the company faced difficulties in reaching the required technological milestones. As of the time of writing, no human missions have yet been undertaken, and the technological hurdles remain significant.
4. The Financial Challenge
Despite the ambitious vision, Mars One faced significant financial hurdles. The cost of sending humans to Mars and building a sustainable colony was projected to be in the billions of dollars. Mars One had initially hoped to raise funds through a combination of private investment, sponsorships, and crowd funding.
However, the company struggled to secure the necessary financing to meet its goals. Investors and industry experts raised concerns about the project’s feasibility, and the financial challenges eventually led to the company scaling back its original plans. Mars One’s inability to secure stable funding became a key factor in its eventual downfall, as the project failed to meet critical deadlines and fell short of its financial targets.
Bas Lansdorp’s Leadership in the Face of Challenges
Despite the financial struggles and the skepticism surrounding the feasibility of Mars One, Bas Lansdorp remained committed to his vision. His leadership was characterized by a passion for space exploration and a desire to push the boundaries of what humanity could achieve. Lansdorp’s resilience in the face of adversity was a testament to his belief in the importance of space exploration for the future of humanity.
However, by 2019, Mars One faced a series of setbacks, including mounting debts, the collapse of key partnerships, and the failure to raise enough capital. The company filed for bankruptcy, marking the end of its ambitious plans. While Mars One’s vision has not yet come to fruition, Bas Lansdorp’s boldness in proposing such an audacious mission has left a lasting impact on the space exploration community and sparked important discussions about the future of Mars exploration.
Legacy and the Future of Mars Exploration
Although Mars One as a company has ceased operations, Bas Lansdorp’s vision and the idea of human settlement on Mars continue to inspire space exploration efforts. The mission sparked interest and investment in Mars exploration, and its challenges have helped inform other ventures, including NASA’s Artemis program and SpaceX’s ambitious plans for Mars colonization.
Lansdorp’s role in advancing the conversation about human exploration of Mars cannot be understated. His willingness to dream big and take risks has paved the way for future endeavors that will one day make Mars exploration a reality.
Conclusion
Bas Lansdorp’s role in Mars One was that of a visionary leader, whose bold dreams and tireless efforts helped bring the idea of human colonization of Mars to the public consciousness. While Mars One may not have achieved its goal of sending humans to the Red Planet, the project’s ambition and innovative approach to space exploration have left an indelible mark on the space industry.
Though the road to Mars remains challenging and full of obstacles, Lansdorp’s work with Mars One continues to inspire the next generation of explorers and dreamers who believe that humanity’s future lies beyond Earth.